Your Car, Built by Robots: The Rise of Industrial Robots in China
How China’s Robots Are Shaping the Future of Manufacturing
Introduction
Forget science fiction—the robot revolution is unfolding today, with China playing a pivotal role. As the world's largest industrial robot market, China accounts for over half of global installations, driving automation across multiple sectors.
China's industrial robot market has grown rapidly, influenced by technology transfer from Japan’s Nachi-Fujikoshi before 2010. Facing limited domestic market share, Nachi-Fujikoshi sold technical documents to China and South Korea, kickstarting robotics development in both nations. While South Korea’s Hyundai Robotics advanced with this technology, China’s reliance on older Nachi-Fujikoshi tech may have contributed to a lingering technological gap with Japan.
China's robotics market is primarily divided into two categories: industrial robots and service robots. Service robots are designed to perform non-industrial tasks in various environments, such as healthcare, logistics, and customer service. Unlike industrial robots, which focus on automation in manufacturing, service robots are often mobile and interact directly with humans or their surroundings. In this issue, we explore in depth the rapidly evolving world of China's industrial robotics.
Industrial robots, defined as multi-jointed mechanical arms or multi-degree-of-freedom devices programmed to perform automated tasks, have become indispensable in modern manufacturing. Their ability to execute repetitive, precise, and often dangerous operations with speed and consistency has revolutionized production processes across industries. By enabling automation, industrial robots enhance efficiency, productivity, and quality while reducing labor costs and mitigating workplace risks.
Domestic companies like Siasun (SHE: 300024, Market cap:$3.88 billion USD), Estun (SHE: 002747, Market cap: $2.13 billion USD), and Inovance (SHE: 300124, Market cap: 21.39 billion USD) are narrowing the technological gap with the “Big Four” (FANUC, ABB, KUKA, and Yaskawa), offering cost-effective, locally tailored solutions while expanding internationally.
Despite robust growth, the market faces challenges. Heavy reliance on imported core components exposes China to supply chain disruptions and geopolitical risks, hindering competitiveness in high-end robotics. Slowing investment in key sectors like automotive and electronics could dampen demand, while growing competition intensifies price pressures, eroding profit margins.
However, the long-term growth potential remains strong. With continued government support, technological advancements, and rising demand from key industries, China's robotics sector is poised for expansion. This dynamic landscape presents significant opportunities for investors eyeing the future of manufacturing.
Industry Overview
Types of industrial robots
Based on their functions, industrial robots can be classified into packaging, loading and unloading, spraying, material handling, welding, grinding, palletizing, and assembly robots. Material handling, welding, and assembly robots are the most commonly used in the industry. Industrial robots can be categorized based on their mechanical structure into articulated robots, SCARA (Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm) robots, parallel robots, Cartesian robots, cylindrical robots, and collaborative robots:
Articulated robots currently dominate the Chinese industrial robot market, holding a 50% to 60% share, according to the China Robotics Industry Alliance (CRIA). Widely used in sectors like automotive, electronics, and metal processing, these robots excel in tasks such as welding, handling, and assembly due to their flexibility and ability to perform complex operations. As China's manufacturing sector continues to automate, articulated robots are expected to remain central to industrial automation.
China Market Size and Forecast
China has held the position of the world's largest industrial robot market since 2013, with its market share growing from 30% in 2013 to over 51% in 2022. This growth is fueled by automation in sectors like automotive, electronics, and emerging industries such as photovoltaics and electric vehicles, according to the International Federation of Robotics (IFR) and the CRIA. In 2023, China’s industrial robot production reached 429,500 units, growing at a compound annual rate of 38% since 2015. Despite a slight slowdown due to factors such as global economic uncertainty, post-pandemic adjustments and supply chain disruptions, production in the first half of 2024 increased by 9.6% year-on-year, reaching 283,200 units. This growth reflects continued strong demand, particularly in downstream sectors, as reported by the National Bureau of Statistics.
The 2024 projection is based on the first half data (283,200 units) doubled to estimate the full year production. The steep curve demonstrates the impressive 38% CAGR since 2015, showing China's rapid advancement in industrial automation.
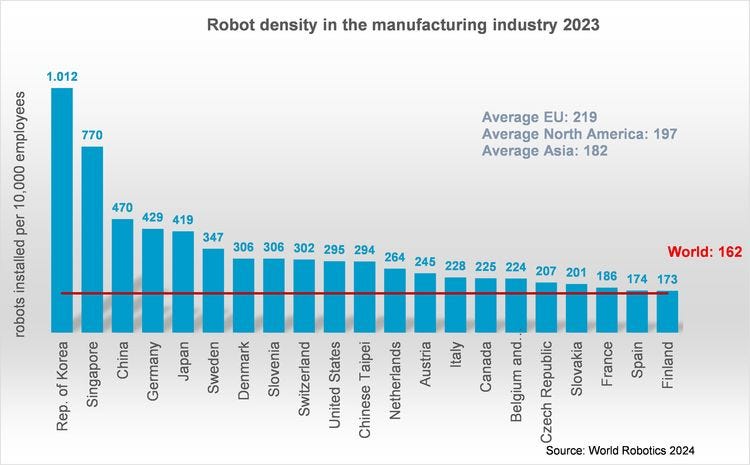
China's industrial robot density has jumped to third place globally. In 2023, the global robot density (the number of industrial robots per 10,000 manufacturing employees) increased from 151 to 162. The countries with the highest robot densities in 2023 were South Korea (1,012 units), Singapore (770 units), China (470 units), Germany (429 units), and Japan (419 units). China's robot density saw a significant increase, rising from 392 units per 10,000 workers in 2022 to 470 units in 2023, a year-on-year growth of 19.9%.
In 2023, the number of newly installed industrial robots in China reached 276,300 units, accounting for 51% of the global total, further solidifying its position as the largest market in the world. While the number of robots in use in China is expected to surpass 2.1 million by the end of 2024, the most recent data available comes from 2023.
Despite short-term challenges like competition and supply chain pressures, China's industrial robot market remains poised for long-term growth, solidifying its global leadership. Government policies supporting automation, along with advancements in 5G, AI, and IoT, are driving expansion. According to CCID Consulting, the market is expected to reach 100 billion RMB ($13.8 billion USD) by 2025, up from 51.07 billion RMB ($7.1 billion USD) in 2023. IFR forecasts annual growth of 5-10%, ensuring China's continued dominance through 2027.